Altman RS, Schwartz RA. Emotionally induced hyperhidrosis. Cutis. 2002 May. 69(5):336-8. [QxMD MEDLINE Link].
Ruchinskas R. Hyperhidrosis and anxiety: chicken or egg?. Dermatology. 2007. 214(3):195-6. [QxMD MEDLINE Link].
Esen AM, Barutcu I, Karaca S, et al. Peripheral vascular endothelial function in essential hyperhidrosis. Circ J. 2005 Jun. 69(6):707-10. [QxMD MEDLINE Link].
Yamashita N, Tamada Y, Kawada M, Mizutani K, Watanabe D, Matsumoto Y. Analysis of family history of palmoplantar hyperhidrosis in Japan. J Dermatol. 2009 Dec. 36(12):628-31. [QxMD MEDLINE Link].
Thirugnanachandran T, Ma H, Phan T. Contralateral hyperhidrosis following lateral medullary infarction. Pract Neurol. 2020 Aug. 20 (4):330-1. [QxMD MEDLINE Link].
Li Z, Chen W, Zhu Y, Han K, Wang J, Chen J, et al. Risk factors and clinical features of paroxysmal sympathetic hyperactivity after spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage. Auton Neurosci. 2020 Jan 27. 225:102643. [QxMD MEDLINE Link].
Rodrigues Masruha M, Lin J, Arita JH, et al. Spontaneous periodic hypothermia and hyperhidrosis: a possibly novel cerebral neurotransmitter disorder. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2011 Apr. 53 (4):378-80. [QxMD MEDLINE Link].
Mehta S, Ralot T, Masatkar V, Agarwal N, Rana A. A curious case of hourly attacks of disabling episodic spontaneous hypothermia with hyperhidrosis. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2015 Mar-Apr. 81(2):185-6. [QxMD MEDLINE Link].
Martín AF, Figueroa SC, Merino Mde L, Hurlee AD. Hyperhidrosis in association with efavirenz. AIDS Patient Care STDS. 2009 Mar. 23(3):143-5. [QxMD MEDLINE Link].
Eustace K, Wilson NJ. Postmenopausal craniofacial hyperhidrosis. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2018 Mar. 43 (2):180-182. [QxMD MEDLINE Link].
Kocyigit P, Akay BN, Saral S, Akbostanci C, Bostanci S. Unilateral hyperhidrosis with accompanying contralateral anhidrosis. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2009 Dec. 34(8):e544-6. [QxMD MEDLINE Link].
Lera M, España A, Idoate MÁ. Focal hyperhidrosis secondary to eccrine naevus successfully treated with botulinum toxin type A. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2015 Aug. 40 (6):640-3. [QxMD MEDLINE Link].
López V, Pinazo I, Santonja N, Jordá E. Eccrine angiomatous hamartoma in a child. Pediatr Dermatol. 2010 Sep-Oct. 27(5):548-9. [QxMD MEDLINE Link].
Sanusi T, Li Y, Sun L, Wang C, Zhou Y, Huang C. Eccrine Angiomatous Hamartoma: A Clinicopathological Study of 26 Cases. Dermatology. 2015. 231 (1):63-9. [QxMD MEDLINE Link].
Shi W, Zhao B, Yao J, et al. Intramedullary Spinal Cord Ganglioglioma Presenting as Hyperhidrosis: A Rare Case Report and Literature Review. World Neurosurg. 2019 Jul. 127:232-6. [QxMD MEDLINE Link].
Ricchetti-Masterson K, Symons JM, Aldridge M, Patel A, Maskell J, Logie J, et al. Epidemiology of hyperhidrosis in 2 population-based health care databases. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018 Feb. 78 (2):358-362. [QxMD MEDLINE Link].
Adar R, Kurchin A, Zweig A, Mozes M. Palmar hyperhidrosis and its surgical treatment: a report of 100 cases. Ann Surg. 1977 Jul. 186(1):34-41. [QxMD MEDLINE Link].
Cloward RB. Hyperhydrosis. J Neurosurg. 1969 May. 30(5):545-51. [QxMD MEDLINE Link].
Cloward RB. Treatment of hyperhidrosis palmaris (sweaty hands); a familial disease in Japanese. Hawaii Med J. 1957 Mar-Apr. 16(4):381-7. [QxMD MEDLINE Link].
Drott C, Gothberg G, Claes G. Endoscopic transthoracic sympathectomy: an efficient and safe method for the treatment of hyperhidrosis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1995 Jul. 33(1):78-81. [QxMD MEDLINE Link].
Saglam M, Esen AM, Barutcu I, et al. Impaired left ventricular filling in patients with essential hyperhidrosis: an echo-Doppler study. Tohoku J Exp Med. 2006 Apr. 208(4):283-90. [QxMD MEDLINE Link].
Tugnoli V, Eleopra R, De Grandis D. Hyperhidrosis and sympathetic skin response in chronic alcoholic patients. Clin Auton Res. 1999 Feb. 9(1):17-22. [QxMD MEDLINE Link].
Moon SY, Shin DI, Park SH, Kim JS. Harlequin syndrome with crossed sympathetic deficit of the face and arm. J Korean Med Sci. 2005 Apr. 20(2):329-30. [QxMD MEDLINE Link]. [Full Text].
Karaca S, Emul M, Kulac M, et al. Temperament and character profile in patients with essential hyperhidrosis. Dermatology. 2007. 214(3):240-5. [QxMD MEDLINE Link].
Walling HW. Clinical differentiation of primary from secondary hyperhidrosis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2011 Apr. 64 (4):690-5. [QxMD MEDLINE Link].
Gross KM, Schote AB, Schneider KK, Schulz A, Meyer J. Elevated social stress levels and depressive symptoms in primary hyperhidrosis. PLoS One. 2014. 9(3):e92412. [QxMD MEDLINE Link]. [Full Text].
Shelley WB, Laskas JJ, Satanove A. Effect of topical agents on planter sweating. AMA Arch Derm Syphilol. 1954 Jun. 69(6):713-6. [QxMD MEDLINE Link].
Qbrexza (glycopyrronium) [package insert]. Menlo Park, Calif: Dermira, Inc. June 2018. Available at [Full Text].
Sofdra (sofpironium topical) [package insert]. Wayne, PA: Botanix SB Inc. June 2024. Available at [Full Text].
Hebert A. Glycopyrronium tosylate for the treatment of primary axillary hyperhidrosis: Pediatric subgroup analyses from the ATMOS-1 and ATMOS-2 Phase 3 randomized controlled trials (Abstract 6659). Presented at the 76th Annual Meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology (AAD). February 16-20, 2018. San Diego, Calif:
Bloudek LM, Gillard KK, Nguyen VB, Klein SZ. Cost-effectiveness of topical glycopyrronium tosylate for the treatment of primary axillary hyperhidrosis. J Med Econ. 2021 Jan-Dec. 24 (1):29-37. [QxMD MEDLINE Link].
Sato K, Kang WH, Saga K, Sato KT. Biology of sweat glands and their disorders. II. Disorders of sweat gland function. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1989 May. 20(5 Pt 1):713-26. [QxMD MEDLINE Link].
Streker M, Reuther T, Verst S, Kerscher M. [Axillary hyperhidrosis--efficacy and tolerability of an aluminium chloride antiperspirant. Prospective evaluation on 20 patients with idiopathic axillary hyperhidrosis]. Hautarzt. 2010 Feb. 61(2):139-44. [QxMD MEDLINE Link].
Yanagishita T, Tamada Y, Ohshima Y, Ito K, Akita Y, Watanabe D. Histological localization of aluminum in topical aluminum chloride treatment for palmar hyperhidrosis. J Dermatol Sci. 2012 Jul. 67 (1):69-71. [QxMD MEDLINE Link].
Sánchez-Carpintero I, Martín-Gorgojo A, Ruiz-Rodríguez R. Microwave Treatment for Axillary Hyperhidrosis and Bromhidrosis. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2017 Jun. 108 (5):418-22. [QxMD MEDLINE Link].
Kaminaka C, Mikita N, Inaba Y, et al. Clinical and histological evaluation of a single high energy microwave treatment for primary axillary hyperhidrosis in Asians: A prospective, randomized, controlled, split-area comparative trial. Lasers Surg Med. 2019 Sep. 51 (7):592-9. [QxMD MEDLINE Link].
Del Boz J, Millán-Cayetano JF, Blázquez-Sánchez N, de Troya M. Individualized Dosing of Oral Oxybutynin for the Treatment of Primary Focal Hyperhidrosis in Children and Teenagers. Pediatr Dermatol. 2016 May. 33 (3):327-31. [QxMD MEDLINE Link].
Klaber M, Catterall M. Treating hyperhidrosis. Anticholinergic drugs were not mentioned. BMJ. 2000 Sep 16. 321(7262):703. [QxMD MEDLINE Link].
Wozniacki L, Zubilewicz T. Primary hyperhidrosis controlled with oxybutynin after unsuccessful surgical treatment. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2009 Dec. 34(8):e990-1. [QxMD MEDLINE Link].
Bouman HD, Lentzer EM. The treatment of hyperhidrosis of hands and feet with constant current. Am J Phys Med. 1952 Jun. 31(3):158-69. [QxMD MEDLINE Link].
Karakoç Y, Aydemir EH, Kalkan MT, Unal G. Safe control of palmoplantar hyperhidrosis with direct electrical current. Int J Dermatol. 2002 Sep. 41(9):602-5. [QxMD MEDLINE Link].
Murphy R, Harrington CI. Treating hyperhidrosis. Iontophoresis should be tried before other treatments. BMJ. 2000 Sep 16. 321(7262):702-3. [QxMD MEDLINE Link].
Sato K, Ohtsuyama M, Samman G. Eccrine sweat gland disorders. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1991 Jun. 24(6 Pt 1):1010-4. [QxMD MEDLINE Link].
Abell E, Morgan K. The treatment of idiopathic hyperhidrosis by glycopyrronium bromide and tap water iontophoresis. Br J Dermatol. 1974 Jul. 91(1):87-91. [QxMD MEDLINE Link].
Siah TW, Hampton PJ. The effectiveness of tap water iontophoresis for palmoplantar hyperhidrosis using a Monday, Wednesday, and Friday treatment regime. Dermatol Online J. 2013 Mar 15. 19(3):14. [QxMD MEDLINE Link].
Ozcan D, Güleç AT. Compliance with tap water iontophoresis in patients with palmoplantar hyperhidrosis. J Cutan Med Surg. 2014 Mar 1. 18(2):109-13. [QxMD MEDLINE Link].
Fujita M, Mann T, Mann O, Berg D. Surgical pearl: use of nerve blocks for botulinum toxin treatment of palmar-plantar hyperhidrosis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2001 Oct. 45(4):587-9. [QxMD MEDLINE Link].
Moraru E, Voller B, Auff E, Schnider P. Dose thresholds and local anhidrotic effect of botulinum A toxin injections (Dysport). Br J Dermatol. 2001 Aug. 145(2):368. [QxMD MEDLINE Link].
Naumann M. Evidence-based medicine: botulinum toxin in focal hyperhidrosis. J Neurol. 2001 Apr. 248 Suppl 1:31-3. [QxMD MEDLINE Link].
Naumann M, Lowe NJ. Botulinum toxin type A in treatment of bilateral primary axillary hyperhidrosis: randomised, parallel group, double blind, placebo controlled trial. BMJ. 2001 Sep 15. 323(7313):596-9. [QxMD MEDLINE Link]. [Full Text].
Kang A, Burns E, Glaser DA. Botulinum toxin A for palmar hyperhidrosis: associated pain, duration, and reasons for discontinuation of therapy. Dermatol Surg. 2015 Feb. 41(2):297-8. [QxMD MEDLINE Link].
Shelley WB, Talanin NY, Shelley ED. Botulinum toxin therapy for palmar hyperhidrosis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1998 Feb. 38(2 Pt 1):227-9. [QxMD MEDLINE Link].
Swartling C, Farnstrand C, Abt G, Stalberg E, Naver H. Side-effects of intradermal injections of botulinum A toxin in the treatment of palmar hyperhidrosis: a neurophysiological study. Eur J Neurol. 2001 Sep. 8(5):451-6. [QxMD MEDLINE Link].
Lecouflet M, Leux C, Fenot M, Célerier P, Maillard H. Duration of efficacy increases with the repetition of botulinum toxin A injections in primary palmar hyperhidrosis: a study of 28 patients. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014 Jun. 70 (6):1083-7. [QxMD MEDLINE Link].
Schnider P, Binder M, Auff E, Kittler H, Berger T, Wolff K. Double-blind trial of botulinum A toxin for the treatment of focal hyperhidrosis of the palms. Br J Dermatol. 1997 Apr. 136(4):548-52. [QxMD MEDLINE Link].
Vadoud-Seyedi J, Simonart T. Treatment of axillary hyperhidrosis with botulinum toxin type A reconstituted in lidocaine or in normal saline: a randomized, side-by-side, double-blind study. Br J Dermatol. 2007 May. 156(5):986-9. [QxMD MEDLINE Link].
Flanagan KH, King R, Glaser DA. Botulinum toxin type a versus topical 20% aluminum chloride for the treatment of moderate to severe primary focal axillary hyperhidrosis. J Drugs Dermatol. 2008 Mar. 7(3):221-7. [QxMD MEDLINE Link].
Woolery-Lloyd H, Elsaie ML, Avashia N. Inguinal hyperhidrosis misdiagnosed as urinary incontinence: treatment with botulinum toxin A. J Drugs Dermatol. 2008 Mar. 7(3):293-5. [QxMD MEDLINE Link].
Gregoriou S, Rigopoulos D, Chiolou Z, Papafragkaki D, Makris M, Kontochristopoulos G. Treatment of bromhidrosis with a glycine-soja sterocomplex topical product. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2011 Mar. 10(1):74-7. [QxMD MEDLINE Link].
Purtuloglu T, Atim A, Deniz S, et al. Effect of radiofrequency ablation and comparison with surgical sympathectomy in palmar hyperhidrosis. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2013 Jun. 43 (6):e151-4. [QxMD MEDLINE Link].
Naeini FF, Saffaei A, Pourazizi M, Abtahi-Naeini B. Histopathological evidence of efficacy of microneedle radiofrequency for treatment of axillary hyperhidrosis. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2015 May-Jun. 81 (3):288-90. [QxMD MEDLINE Link].
Kumagai K, Kawase H, Kawanishi M. Health-related quality of life after thoracoscopic sympathectomy for palmar hyperhidrosis. Ann Thorac Surg. 2005 Aug. 80(2):461-6. [QxMD MEDLINE Link].
Kotzareff A. Resection partielle de trone sympathetique cervical droit pour hyperhidrose unilaterale. Rev Med Suisse Romande. 1920. 40:111-3.
Chen HJ, Lu K, Liang CL. Transthoracic endoscopic T-2, 3 sympathectomy for facial hyperhidrosis. Auton Neurosci. 2001 Oct 8. 93(1-2):91-4. [QxMD MEDLINE Link].
Hsu CP, Shia SE, Hsia JY, Chuang CY, Chen CY. Experiences in thoracoscopic sympathectomy for axillary hyperhidrosis and osmidrosis: focusing on the extent of sympathectomy. Arch Surg. 2001 Oct. 136(10):1115-7. [QxMD MEDLINE Link].
Kim BY, Oh BS, Park YK, Jang WC, Suh HJ, Im YH. Microinvasive video-assisted thoracoscopic sympathicotomy for primary palmar hyperhidrosis. Am J Surg. 2001 Jun. 181(6):540-2. [QxMD MEDLINE Link].
Vasconcelos CFM, Aguiar WS, Cordeiro GG, Silveira KC, Moreira RS, Lisboa DL, et al. Modified R5-R8 Thoracic Sympathectomy for Severe Compensatory Hyperhidrosis. Ann Thorac Surg. 2021 Jan. 111 (1):e57-e59. [QxMD MEDLINE Link].
Panhofer P, Zacherl J, Jakesz R, Bischof G, Neumayer C. Improved quality of life after sympathetic block for upper limb hyperhidrosis. Br J Surg. 2006 May. 93(5):582-6. [QxMD MEDLINE Link].
Lai YT, Yang LH, Chio CC, Chen HH. Complications in patients with palmar hyperhidrosis treated with transthoracic endoscopic sympathectomy. Neurosurgery. 1997 Jul. 41(1):110-3; discussion 113-5. [QxMD MEDLINE Link].
Chwajol M, Barrenechea IJ, Chakraborty S, Lesser JB, Connery CP, Perin NI. Impact of compensatory hyperhidrosis on patient satisfaction after endoscopic thoracic sympathectomy. Neurosurgery. 2009 Mar. 64(3):511-8; discussion 518. [QxMD MEDLINE Link].
Chou SH, Kao EL, Li HP, Lin CC, Huang MF. T4 sympathectomy for palmar hyperhidrosis: an effective approach that simultaneously minimzes compensatory hyperhidrosis. Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 2005 Jul. 21(7):310-3. [QxMD MEDLINE Link].
Heckmann M. Complications in patients with palmar hyperhidrosis treated with transthoracic endoscopic sympathectomy. Neurosurgery. 1998 Jun. 42(6):1403-4. [QxMD MEDLINE Link].
Li X, Tu YR, Lin M, Lai FC, Chen JF, Miao HW. Minimizing endoscopic thoracic sympathectomy for primary palmar hyperhidrosis: guided by palmar skin temperature and laser Doppler blood flow. Ann Thorac Surg. 2009 Feb. 87(2):427-31. [QxMD MEDLINE Link].
Neves S, Uchoa PC, Wolosker N, et al. Long-term comparison of video-assisted thoracic sympathectomy and clinical observation for the treatment of palmar hyperhidrosis in children younger than 14. Pediatr Dermatol. 2012 Sep-Oct. 29 (5):575-9. [QxMD MEDLINE Link].
Kim WO, Kil HK, Yoon KB, Yoon DM. Topical glycopyrrolate for patients with facial hyperhidrosis. Br J Dermatol. 2008 May. 158(5):1094-7. [QxMD MEDLINE Link].
Goldman A, Wollina U. Subdermal Nd-YAG laser for axillary hyperhidrosis. Dermatol Surg. 2008 Jun. 34(6):756-62. [QxMD MEDLINE Link].
Junsuwan N, Manuskiatti W, Phothong W, Wanitphakdeedecha R. Fractional CO2 laser-assisted Botulinum toxin type A delivery for the treatment of primary palmar hyperhidrosis. Lasers Med Sci. 2021 Feb. 36 (1):233-236. [QxMD MEDLINE Link].
Schick CH, Grallath T, Schick KS, Hashmonai M. Radiofrequency Thermotherapy for Treating Axillary Hyperhidrosis. Dermatol Surg. 2016 May. 42 (5):624-30. [QxMD MEDLINE Link].
Lillis PJ, Coleman WP 3rd. Liposuction for treatment of axillary hyperhidrosis. Dermatol Clin. 1990 Jul. 8(3):479-82. [QxMD MEDLINE Link].
Na GY, Park BC, Lee WJ, Park DJ, Kim do W, Kim MN. Control of palmar hyperhidrosis with a new "dry-type" iontophoretic device. Dermatol Surg. 2007 Jan. 33(1):57-61. [QxMD MEDLINE Link].
Choi YH, Lee SJ, Kim do W, Lee WJ, Na GY. Open clinical trial for evaluation of efficacy and safety of a portable "dry-type" iontophoretic device in treatment of palmar hyperhidrosis. Dermatol Surg. 2013 Apr. 39(4):578-83. [QxMD MEDLINE Link].
Millán-Cayetano JF, Del Boz J, Toledo-Pastrana T, Nieto-Guindo M, García-Montero P, de Troya-Martín M. Initial study of transdermal oxybutynin for treating hyperhidrosis. J Dermatol. 2017 Jun. 44 (6):717-20. [QxMD MEDLINE Link].
Nguyen NV, Gralla J, Abbott J, Bruckner AL. Oxybutynin 3% gel for the treatment of primary focal hyperhidrosis in adolescents and young adults. Pediatr Dermatol. 2018 Mar. 35 (2):208-12. [QxMD MEDLINE Link].
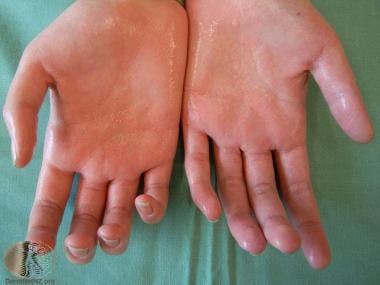 Hyperhidrosis of the palms. Courtesy of DermNet New Zealand (https://www.dermnetnz.org/assets/Uploads/hair-nails-sweat/hyperhidrosis.jpg).
Hyperhidrosis of the palms. Courtesy of DermNet New Zealand (https://www.dermnetnz.org/assets/Uploads/hair-nails-sweat/hyperhidrosis.jpg).

