Sloan MA, Alexandrov AV, Tegeler CH, et al. Assessment: transcranial Doppler ultrasonography: report of the Therapeutics and Technology Assessment Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology. Neurology. 2004 May 11. 62(9):1468-81. [QxMD MEDLINE Link].
Ntaios G, Papavasileiou V, Sagris D, et al. Closure of patent foramen ovale versus medical therapy in patients with cryptogenic stroke or transient ischemic attack: updated systematic review and meta-analysis. Stroke. 2018 Feb. 49(2):412-8. [QxMD MEDLINE Link]. [Full Text].
Alberts MJ. Adding patent foramen ovale closure to antiplatelet drugs reduced ischemic stroke after cryptogenic stroke. Ann Intern Med. 2018 Jan 16. 168(2):JC6. [QxMD MEDLINE Link].
Saver JL, Mattle HP, Thaler D. Patent foramen ovale closure versus medical therapy for cryptogenic ischemic stroke: a topical review. Stroke. 2018 Jun. 49(6):1541-8. [QxMD MEDLINE Link]. [Full Text].
Garg A, Thawabi M, Rout A, Sossou C, Cohen M, Kostis JB. Recurrent stroke reduction with patent foramen ovale closure versus medical therapy based on patent foramen ovale characteristics: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Cardiology. 2019. 144(1-2):40-9. [QxMD MEDLINE Link].
Carroll AM, Carroll JD. Device closure of patent foramen ovale for cryptogenic stroke: patient selection and outcomes according to new randomized trials. Curr Cardiol Rep. 2019 Apr 22. 21(6):48. [QxMD MEDLINE Link].
Hagen PT, Scholz DG, Edwards WD. Incidence and size of patent foramen ovale during the first 10 decades of life: an autopsy study of 965 normal hearts. Mayo Clin Proc. 1984 Jan. 59(1):17-20. [QxMD MEDLINE Link].
Schneider B, Hofmann T, Justen MH, Meinertz T. Chiari's network: normal anatomic variant or risk factor for arterial embolic events?. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1995 Jul. 26(1):203-10. [QxMD MEDLINE Link].
Khositseth A, Cabalka AK, Sweeney JP, et al. Transcatheter Amplatzer device closure of atrial septal defect and patent foramen ovale in patients with presumed paradoxical embolism. Mayo Clin Proc. 2004 Jan. 79(1):35-41. [QxMD MEDLINE Link].
Attenhofer Jost CH, Connolly HM, O'Leary PW, Warnes CA, Tajik AJ, Seward JB. Left heart lesions in patients with Ebstein anomaly. Mayo Clin Proc. 2005 Mar. 80(3):361-8. [QxMD MEDLINE Link].
[Guideline] Lopez L, Saurers DL, Barker PCA, et al. Guidelines for performing a comprehensive pediatric transthoracic echocardiogram: recommendations from the American Society of Echocardiography. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2024 Feb. 37 (2):119-70. [QxMD MEDLINE Link]. [Full Text].
[Guideline] Diener HC, Akagi T, Durongpisitkul K,et al. Closure of the patent foramen ovale in patients with embolic stroke of undetermined source: A clinical expert opinion and consensus statement for the Asian-Pacific region. Int J Stroke. 2020 Dec. 15 (9):937-44. [QxMD MEDLINE Link].
[Guideline] Aplin M, Andersen A, Brandes A, et al. Assessment of patients with a suspected cardioembolic ischemic stroke. A national consensus statement. Scand Cardiovasc J. 2021 Oct. 55 (5):315-25. [QxMD MEDLINE Link]. [Full Text].
[Guideline] Cantinotti M, Di Salvo G, Voges I, et al, for the members of the 2022–2024 EACVI Scientific Documents Committee. Standardization in paediatric echocardiographic reporting and critical interpretation of measurements, functional parameters, and prediction scores: a clinical consensus statement of the European Association of Cardiovascular Imaging of the European Society of Cardiology and the Association for European Paediatric and Congenital Cardiology. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2024 Jul 31. 25 (8):1029-50. [QxMD MEDLINE Link]. [Full Text].
[Guideline] Caso V, Turc G, Abdul-Rahim AH, et al. European Stroke Organisation (ESO) Guidelines on the diagnosis and management of patent foramen ovale (PFO) after stroke. Eur Stroke J. 2024 Dec. 9 (4):800-34. [QxMD MEDLINE Link]. [Full Text].
Lanzone AM, Castelluccio EV, Della Pina P, Boldi E, Lussardi G, Frati G, et al. Comparative diagnostic accuracy of transcranial Doppler and contrast-enhanced transthoracic echocardiography for the diagnosis of patent foramen ovale and atrial septal defect. Panminerva Med. 2024 Jun. 66 (2):124-30. [QxMD MEDLINE Link].
Furlan AJ, Reisman M, Massaro J, et al; Closure I Investigators. Closure or medical therapy for cryptogenic stroke in patent foramen ovale. N Eng J Med. 2012 Mar 15. 366 (11):991-9.
Meier B, Kalesan B, Mattle HP, et al; PC Trial Investigators. Percutanous closure of patent foramen ovale in cryptogenic embolism. N Engl J Med. 2013 Mar 21. 368(12):1083-91.
Saver JL, Carroll JD, Thaler DE, et all ; RESPECT Investigators. Long-Term outcomes of Patent Foramen Ovale Closure or Medical Theaapy after Stroke. N Eng J Med. 2017 Sept 14. 377:1022-32.
Sondergaard L, Kasner SE, Rhodes JF, et al; Gore REDUCE Investigators. Patent Foramen Ovale Closure or Antiplatelet Therapy for Cryptogenic Stroke. N Eng J Med. 2017 Sept 14. 377:1033-42.
Mas JL, Derumeauz G, Guillon B, et al; CLOSE Investigators. Patent Foramen Ovale Closure or Anticoagulation vs. Antiplatelet after stroke. N Eng J Med. 2017 Sep 14. 377 (11):1011-21.
Sørensen H, Grove EL, Hojbjerg JA, Andersen A, Nielsen-Kudsk JE, Simonsen CZ. Recurrent ischemic stroke/transient ischemic attack after patent foramen ovale closure: A cohort study. Int J Stroke. 2024 Sep 20. 17474930241281120. [QxMD MEDLINE Link].
Bonnesen K, Korsholm K, Andersen A, et al. Risk of ischemic stroke after patent foramen ovale closure. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2024 Oct 8. 84 (15):1424-33. [QxMD MEDLINE Link].
Asghar A, Canthiya L, Khachatrian A, et al. Long-term cerebrovascular outcomes of patients undergoing percutaneous patent foramen ovale closure in observational studies: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2024 Dec 10. 34 (2):108189. [QxMD MEDLINE Link]. [Full Text].
Agostoni P, Gasparini G, Destro G. Acute myocardial infarction probably caused by paradoxical embolus in a pregnant woman. Heart. 2004 Mar. 90(3):e12. [QxMD MEDLINE Link]. [Full Text].
Diaz Castro O, Bueno H, Nebreda LA. Acute myocardial infarction caused by paradoxical tumorous embolism as a manifestation of hepatocarcinoma. Heart. 2004 May. 90(5):e29. [QxMD MEDLINE Link]. [Full Text].
Pell AC, Hughes D, Keating J, Christie J, Busuttil A, Sutherland GR. Brief report: fulminating fat embolism syndrome caused by paradoxical embolism through a patent foramen ovale. N Engl J Med. 1993 Sep 23. 329(13):926-9. [QxMD MEDLINE Link].
Bonati LH, Wetzel SG, Kessel-Schaefer A, Buser P, Lyrer PA, Engelter ST. Diffusion-weighted imaging findings differ between stroke attributable to spontaneous cervical artery dissection and patent foramen ovale. Eur J Neurol. 2010 Feb. 17(2):307-13. [QxMD MEDLINE Link].
[Guideline] Stout KK, Daniels CJ, Aboulhosn JA, et al. 2018 AHA/ACC Guideline for the Management of Adults with Congenital Heart Disease: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2018 Aug 10. [QxMD MEDLINE Link]. [Full Text].
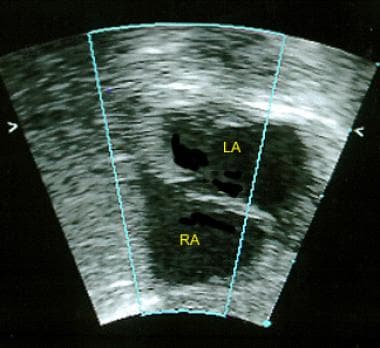 This 2-dimensional echocardiogram in an infant (subcostal long-axis view) shows a patent foramen ovale. Right atrium (RA) and left atrium (LA
This 2-dimensional echocardiogram in an infant (subcostal long-axis view) shows a patent foramen ovale. Right atrium (RA) and left atrium (LA








