Practice Essentials
Takayasu arteritis is a rare, systemic, inflammatory large-vessel vasculitis of unknown etiology that most commonly affects women of childbearing age. [1, 2] It is defined as "granulomatous inflammation of the aorta and its major branches" by the Chapel Hill Consensus Conference on the Nomenclature of Systemic Vasculitis. [3] See the image below. (See Etiology and Epidemiology.)
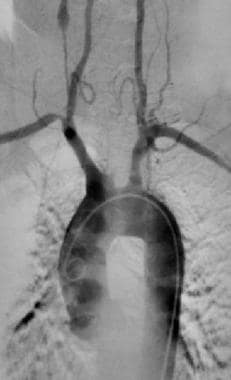 Takayasu arteritis. Complete occlusion of the left common carotid artery in a 48-year-old woman with Takayasu disease. Also note narrowing of the origin of the right subclavian artery and a narrowed small vessel with subsequent aneurysmal dilatation on the right side. Image courtesy of Robert Cirillo, MD.
Takayasu arteritis. Complete occlusion of the left common carotid artery in a 48-year-old woman with Takayasu disease. Also note narrowing of the origin of the right subclavian artery and a narrowed small vessel with subsequent aneurysmal dilatation on the right side. Image courtesy of Robert Cirillo, MD.
Takayasu arteritis commonly occurs in woman younger than age 50 years; however, it has been reported in patients as young as age 6 months. Takayasu arteritis can manifest as isolated, atypical, and/or catastrophic disease. It can involve any or all of the major organ systems. The disease has been reported in all parts of the world, although it appears to be more prevalent in Asians. (See Epidemiology.)
Signs and symptoms
Approximately 10% of patients with Takayasu arteritis are asymptomatic. Clinical manifestations are heterogeneous and include the following:
-
Systemic (eg, malaise, arthralgias, fever) - May precede clinical vascular involvement
-
Cardiac and vascular (eg, bruit, especially carotid; blood pressure difference in extremities; claudication; hypertension)
-
Neurologic (eg, headache, visual disturbance)
-
Dermatologic (eg, erythema nodosum)
See Presentation for more detail.
Diagnosis
In the American College of Rheumatology/European Alliance of Associations for Rheumatology classification criteria for Takayasu arteritis, absolute requirements are age ≤60 years at diagnosis and evidence of vasculitis in the aorta or branch arteries, confirmed by vascular imaging. Additional criteria are assigned points; a cumulative score of ≥5 points has sensitivity of 93.8% and specificity of 99.2%. [4] Criteria and points assigned are as follows:
-
Female sex (1 point)
-
Angina (2)
-
Limb claudication (2)
-
Arterial bruit (2)
-
Reduced upper extremity pulse (2)
-
Reduced pulse or tenderness of a carotid artery (2)
-
Blood pressure difference between arms of ≥20 mm Hg (1)
-
Number of affected arterial territories (1 to 3)
-
Paired artery involvement (1)
-
Abdominal aorta plus renal or mesenteric involvement (3)
Takayasu arteritis can be divided into the following six types based on angiographic involvement [5] :
-
Type I - Branches of the aortic arch
-
Type IIa - Ascending aorta, aortic arch, and its branches
-
Type IIb - Type IIa region plus thoracic descending aorta
-
Type III - Thoracic descending aorta, abdominal aorta, renal arteries, or a combination
-
Type IV - Abdominal aorta, renal arteries, or both
-
Type V - Entire aorta and its branches
See Presentation and Workup for more detail.
Treatment
Corticosteroids are the mainstay of therapy for active Takayasu arteritis. However, some patients may also require cytotoxic agents, to achieve remission and taper of long-term corticosteroid treatment. Biologic agents (eg, tocilizumab, tumor necrosis factor inhibitors) are added in active disease and refractory cases.
See Treatment and Medication for more detail.
For patient education information, see Arthritis and Takayasu's Arteritis.
Background
Takayasu arteritis is named in honor of Japanese ophthalmologist Mikito Takayasu, who first reported a case of the disease in 1905. His patient was a 21-year-old woman with retinal vessel changes and decreased pulses in branches of the aortic arch. Such ophthalmologic findings are rarely encountered and are not included in the American College of Rheumatology criteria for the disorder. [6]
Shimizu and Sano reported six cases of Takayasu arteritis in an English-language publication in 1951, terming the disorder "pulseless disease because of an absence of radial pulse in their patients. This led to a misunderstanding ot Takayasu arteritis as a disorder of only locally limited involvement. [6]
Pathophysiology
Takayasu arteritis is an inflammatory disease of large- and medium-sized arteries, with a predilection for the aorta and its branches. Advanced lesions demonstrate a panarteritis with intimal proliferation.
Lesions produced by the inflammatory process can be stenotic, occlusive, or aneurysmal. All aneurysmal lesions may have areas of arterial narrowing. Vascular changes lead to the main complications, including hypertension, most often due to renal artery stenosis or, more rarely, stenosis of the suprarenal aorta; aortic insufficiency due to aortic valve involvement; pulmonary hypertension; and aortic or other arterial aneurysm.
The renal arteries are involved in 24% to 68% of Takayasu arteritis cases. Renal artery involvement is often bilateral. Patients with renal artery involvement typically have coexistent stenosis of the perirenal aorta. [7]
Congestive heart failure is a common finding, much more so than dilated cardiomyopathy, myocarditis, and pericarditis, which also have been reported. In patients with pulmonary artery involvement, the right artery appears to be affected more than the left, Complications of pulmonary artery involvement include pneumonia, interstitial pulmonary fibrosis, and alveolar damage.
Other pathophysiologic consequences include hypotensive ischemic retinopathy, vertebrobasilar ischemia, microaneurysms, carotid stenosis, hypertensive encephalopathy, and inflammatory bowel disease. Rarely, Takayasu arteritis has also been associated with glomerulonephritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, polymyositis, polymyalgia rheumatica, rheumatoid arthritis, Still disease, and ankylosing spondylitis.
Etiology
The etiology of Takayasu arteritis is unknown. The underlying pathologic process is inflammatory, with several etiologic factors having been proposed, including infection with spirochetes, Mycobacterium tuberculosis, and streptococcal organisms; and circulating antibodies due to an autoimmune process. Genetic susceptibility factors have been identified. [8, 9]
An antigen may stimulate aortic tissue, leading to the expression of heat shock protein–65, which, in turn, induces major histocompatibility (MHC) class I–related chain A (MICA). Natural killer cells and gamma-delta T cells expressing NKG2D receptors may infiltrate and recognize MICA on vascular smooth muscle cells, leading to acute inflammation. Proinflammatory cytokines are also released from the natural killer and T cells, inducing the production of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) and amplifying the inflammatory response. This, in turn, would induce more MHC antigen and stimulate molecule expression on vascular cells, recruiting more mononuclear cells.
Histocompatibility complexes are activated through Toll-like receptors. Th1 lymphocytes, through interferon gamma, activate macrophages, which, in turn, release vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF). This ultimately results in smooth muscle migration and intimal proliferation. Th17 cells induced by the interleukin (IL)–23 microenvironment also contribute to vascular lesions through activation of infiltrating neutrophils.
The cellular infiltrate in Takayasu arteritis contains about 15% each of CD4+ and CD8+ T cells. IL-6 is a proinflammatory cytokine mainly synthesized by activated monocytes, macrophages, and T cells. IL-6 activates B cells and enhances T-cell cytotoxicity, natural killer cell activity, fibroblast proliferation, and acute-phase protein synthesis. Amplification of proinflammatory cytokine genes from aortic tissue reveals strong expression of IL-6 transcripts.
In a case report, M tuberculosis and its 65-kd heat shock protein was implicated in the etiology. Patients with Takayasu arteritis were found to have higher immunoglobulin G (IgG), immunoglobulin M (IgM), and immunoglobulin A (IgA) titers against the M tuberculosis extract than did patients without the condition. [10]
One article reported the presence of CD3+ T cells and IgG antibodies reactive to circulating antimycobacterial heat shock protein 65 (mHSP65) antibodies and to its human homologue, hHSP60. [11] This suggests a possible cross-reactivity of immune response between mHSP65 and hHSP60. Case reports suggesting the role of antiendothelial cell, anticardiolipin, and antiaorta antibodies also exist.
The genetic susceptibility factor that has been most consistently associated with Takayasu arteritis is the human leukocyte antigen (HLA) allele HLA-B*52, which has been confirmed in several ethnicities. HLA-B*52 has a higher prevalence in Asians, which may help explain the greater frequency of Takayasu arteritis in this population. [8, 9] Carriage of HLA-B∗52 is associated with more severe disease, with a higher incidence of left ventricular wall abnormalities and aortic regurgitation, and earlier disease onset. [12]
Other HLA alleles have also been implicated; for example, HLA-B∗39, HLA-DRB1∗1502, and HLA-DRB1∗0405 have also been associated with the disease in Japanese patients. HLA-B*39 is associated with renal artery stenosis. [12] In addition, genome-wide association studies have identified several non-HLA susceptibility loci. [9]
One study demonstrated an association between several cases of Takayasu arteritis and CD36 deficiency (CD36d). [13] The human CD36 antigen is a multifunctional membrane glycoprotein that belongs to the class B scavenger receptor family. It is expressed on monocytes, platelets, and endothelial cells, and contributes to myocardial fatty acid transport. In patients with CD36d, myocardial I-15-(p-iodophenyl)-3-(R,S)-methyl pentadecanoic acid (BMIPP) uptake was absent.
Epidemiology
Occurrence in the United States
Takayasu arteritis is estimated to affect 2.6 persons per million annually. The prevalence is 2.6-6.4 persons per million population. Any discrepancy in terms of pinpointing the prevalence is attributed to genetic factors and difficulty in diagnosis.
Between 1971 and 1983 in Olmsted County, Minnesota, three cases were recorded, thus establishing an annual incidence of 2.6 cases per million population. [14]
International occurrence
Worldwide incidence of Takayasu arteritis is estimated at 2.6 cases per million per year. Although the disease has a worldwide distribution, it is observed more frequently in Asian countries such as Japan, Korea, China, India, Thailand, and Singapore, as well as in Turkey, Israel, and Central and South America. About 100-200 new cases of Takayasu arteritis are registered each year in Japan. [6]
Estimates of the incidence rates in Europe vary from 0.4 to 1.5 per million, while the prevalence ranges from 4.7 to 33 per million. [15] It is unclear whether the variations reflect geographical and genetic differences among the populations or methodological differences in epidemiologic studies. [15]
Race-, sex-, and age-related demographics
Takayasu arteritis is observed more frequently in patients of Asian or Indian descent. Japanese patients with Takayasu arteritis have a higher incidence of aortic arch involvement. In contrast, series from India report higher incidences of abdominal involvement. [6, 16]
Approximately 80% of patients with Takayasu arteritis are women; however, the high female-to-male ratio seems to decrease west of Japan. In India, the female-to-male ratio is as low as 1.6:1. [6]
Most patients with Takayasu arteritis are aged 4-63 years, with the mean age of onset being approximately 30 years. Fewer than 15% of cases present in individuals older than 40 years.
Prognosis
Takayasu arteritis is associated with substantial morbidity and may be life-threatening. Its course usually extends for many years, with varying degrees of activity. Approximately 20% of patients have a monophasic and self-limited disease. In others, Takayasu arteritis is progressive or relapsing/remitting and requires immunosuppressive treatment. [17, 18, 19]
A National Institutes of Health study of 60 patients with Takayasu arteritis showed that 20% of patients had a monophasic illness, self-limiting illness and therefore did not require immunosuppressive treatment. In the remaining 80% of patients, who did not have a monophasic illness and who experienced a single exacerbation, immunosuppressive therapy resulted in remission in 60%. Of these, one half experienced relapse after immunosuppressive therapy was stopped. [20]
Complications
The overall morbidity in Takayasu arteritis depends on the severity of the lesions and their consequences. Complications of the disease include the following:
-
Stroke
-
Intracranial hemorrhage
-
Seizures
-
Graft stenosis and/or occlusion
-
Ischemia
-
Organ failure
-
Complications of hypertension (eg, aortic dissection [21] )
-
Fetal injury
-
Valvular heart disease
-
Retinopathy
-
Renovascular hypertension
Long-term use of corticosteroids can lead to infection, adrenal suppression, cataracts, hyperglycemia, hypertension (which complicates blood pressure control), osteoporosis, and aseptic necrosis.
Morbidity and mortality
Takayasu arteritis is a chronic relapsing and remitting disorder. The overall 10-year survival rate is approximately 90%; however, this rate is reduced in the presence of major complications. [17] The 5- and 10-year survival rates are approximately 69% and 36%, respectively, in patients with 2 or more complications. The 5- and 10-year survival rates associated with 1 or fewer complications are 100% and 96%, respectively. [22]
Strict management of traditional cardiovascular risk factors such as dyslipidemia, hypertension, and lifestyle factors that increase the risk of cardiovascular disease is mandatory to minimize secondary cardiovascular complications. These complications are the major cause of death in Takayasu arteritis.
A 2008 study assessing quality of life with Takayasu arteritis showed worse scores for physical and mental health compared with many other chronic diseases associated with peripheral vascular disease. Disease remission is the only factor that positively influences physical and mental quality of life. [23] Patients with rheumatoid arthritis or ankylosing spondylitis rated their quality of life as similar to those with Takayasu arteritis. [24]
Patient Education
Patients need to understand the nature of the disease and the need to take medications to prevent complications. When in remission or when experiencing mild forms of Takayasu arteritis, patients are tempted to stop antihypertensive drugs, thus increasing their risk of serious neurologic and other systemic complications.
For patient education information, see Arthritis and Takayasu's Arteritis.
-
Takayasu arteritis. Complete occlusion of the left common carotid artery in a 48-year-old woman with Takayasu disease. Also note narrowing of the origin of the right subclavian artery and a narrowed small vessel with subsequent aneurysmal dilatation on the right side. Image courtesy of Robert Cirillo, MD.
-
Takayasu arteritis. Characteristic long, tapered narrowing of the distal aorta and iliac vessels. Image courtesy of Robert Cirillo, MD.
-
Takayasu arteritis. Image obtained in the same patient as in Image 2 reveals narrowing of the proximal descending aorta and right brachiocephalic artery. Image courtesy of Robert Cirillo, MD.
-
Takayasu arteritis. Aortogram of a 15-year-old girl with Takayasu arteritis. Note large aneurysms of descending aorta and dilatation of innominate artery. Image courtesy of Christine Hom, MD.
-
Takayasu arteritis. MRI of thorax of 15-year-old girl with Takayasu arteritis. Note aneurysms of descending aorta. Image courtesy of Christine Hom, MD.
-
Takayasu arteritis. Coronal MRI of abdomen of 15-year-old girl with Takayasu arteritis. Note thickening and tortuosity of abdominal aorta proximal to kidneys. Image courtesy of Christine Hom, MD.








