Practice Essentials
A Stener lesion occurs when the thumb is forcefully abducted and the distal attachment of the ulnar collateral ligament (UCL) at the metacarpophalangeal (MCP) joint is traumatically avulsed from its insertion into the base of the proximal phalanx of the thumb. [1, 2] The avulsed end of the UCL gets caught under the proximal edge of the adductor aponeurosis and folds into itself as the thumb returns to its normal position. The displacement of the avulsed UCL from its insertion ultimately results in thumb MCP joint instability to valgus stress.
In his now classic 1962 article, Stener described a distinct, surgically correctable anatomic lesion that could account for the chronic instability found in the thumbs of some gamekeepers and skiers. [3] Campbell first coined the term gamekeeper's thumb in 1955, when he described insufficiency in the UCL of the thumb MCP joint in many Scottish gamekeepers. [4]
The proposed etiology of this laxity was related to the method used by gamekeepers to kill wounded rabbits. A gamekeeper would hold the rabbit's legs in one hand and wedge the animal's neck in the cleft between the thumb and index finger of the other hand. By forcefully pulling on the rabbit's legs, the neck was stretched and extended against the ulnar side of the thumb, thus breaking the neck and killing the rabbit.
Anatomy
The clearest and most eloquent anatomic depiction of the Stener lesion can be found in Stener's 1962 article. [3] Most of the material included here is adapted from his original work.
Important structures around the MCP joint include the adductor aponeurosis and tendon, the dorsal aponeurosis, the collateral ligament proper, and the accessory collateral ligament of the thumb. The adductor aponeurosis serves as an active restraint to thumb abduction but has no passive role in MCP stability. Severance of the adductor aponeurosis has no effect on lateral stability.
The UCL of the thumb is composed of two discernible components: accessory and proper. In his cadaveric dissections, Stener found that the UCL proper was taut in flexion and loose in extension, whereas the opposite was true for the accessory UCL. Transection of the UCL proper resulted in increased abduction when the MCP joint was flexed but not when the joint was held in the extended position. This instability was found to be slight and did not become severe until the accessory UCL was severed as well. The volar plate restricted abduction when the MCP joint was extended, even when both the UCL proper and the UCL accessory were severed.
The UCL provides lateral support and prevents volar subluxation of the MCP joint. Stability of the thumb MCP joint to abduction is vital for key pinch, tip pinch, and thumb opposition.
Pathophysiology
Stener described a lesion produced by forced thumb abduction in which the distal attachment of the UCL was traumatically avulsed from the proximal phalanx of the thumb. The severed end would become caught under the adductor aponeurosis and would therefore be unable to return to its anatomic position. Consequently, the severed ligament would fold on itself and thus would be prevented from healing and restoring stability to the MCP joint (see the image below).
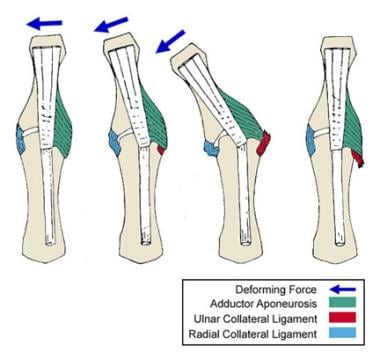 Displacement of the ulnar collateral ligament by the adductor aponeurosis during hyperabduction of the thumb.
Displacement of the ulnar collateral ligament by the adductor aponeurosis during hyperabduction of the thumb.
With a Stener lesion, a situation exists in which the MCP joint of the thumb is rendered permanently unstable because the UCL is prevented from healing by the interposed adductor aponeurosis. The resultant chronic instability significantly impairs function in the injured hand.
Prognosis
Stener's original article was a significant contribution to the treatment of acute disruptions of the UCL of the thumb MCP joint. If a Stener lesion is recognized early, the UCL may be reduced operatively and secured in its anatomic position. Early recognition and anatomic reduction can result in excellent functional outcome in the vast majority of cases. Late presentation or a delayed diagnosis of a Stener lesion may produce a need for more involved surgery, with less desirable results.
-
Displacement of the ulnar collateral ligament by the adductor aponeurosis during hyperabduction of the thumb.
-
Stress view of ulnar collateral ligament.
-
Ruptured ulnar collateral ligament.
-
Completed repair using suture anchors for fixation.

