Practice Essentials
Compromise of the blood supply from microvascular disease, often in association with lack of sensation because of neuropathy, predisposes persons with diabetes mellitus to foot infections. These infections span the spectrum from simple, superficial cellulitis to chronic osteomyelitis.
The radiograph below demonstrates a foot lesion in a patient with diabetes.
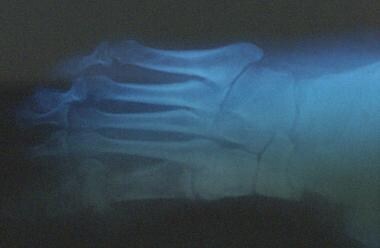 Chronic diabetic ulceration with underlying osteomyelitis. Plain film radiograph exhibiting cortical disruption at the medial aspect of the first MTP joint.
Chronic diabetic ulceration with underlying osteomyelitis. Plain film radiograph exhibiting cortical disruption at the medial aspect of the first MTP joint.
Signs and symptoms
Diabetic foot infections typically take one of the following forms:
-
Cellulitis
-
Deep-skin and soft-tissue infections
-
Acute osteomyelitis
-
Chronic osteomyelitis
Cellulitis
-
Tender, erythematous, nonraised skin lesions are present, sometimes with lymphangitis
-
Lymphangitis suggests group A streptococcal infection
-
Bullae are typical of Staphylococcus aureus infection, but occasionally occur with group A streptococci
· No ulcer or wound exudate is present
Deep-skin and soft-tissue infections
-
The patient may be acutely ill, with painful induration of the soft tissues in the extremity
-
Wound discharge is usually not present but may be foul smelling when it is
-
In mixed infections that may involve anaerobes, crepitation may be noted over the afflicted area
-
Extreme pain and tenderness may indicate compartment syndrome or clostridial infection (ie, gas gangrene)
-
The tissues are not tense, and bullae may be present
Acute osteomyelitis
-
Unless peripheral neuropathy is present, the patient has pain at the site of the involved bone
-
Symptoms are usually present for 10-14 days
-
Usually, fever and regional adenopathy are absent
Chronic osteomyelitis
-
The patient's temperature is usually less than 102°F
-
Discharge is commonly foul
-
No lymphangitis is observed
-
Pain may or may not be present, depending on the degree of peripheral neuropathy
-
Deep, penetrating ulcers and deep sinus tracts (diagnostic of chronic osteomyelitis) are usually located between the toes or on the plantar surface of the foot
-
The medial malleoli, shins, or heels are not usually sites of involvement
-
Symptoms may be present for several weeks
See Clinical Presentation for more detail.
Diagnosis
Cellulitis
-
The white blood cell (WBC) count and erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) are slightly or moderately elevated, but these elevations are not diagnostic
-
Blood culture results are usually negative; if positive, they usually indicate the presence of group A or group B streptococci
Cultures of skin via aspiration or biopsy are generally unrewarding; aspiration of a sample from the leading edge of the erythematous border has a low yield (likely < 5%) but may be used if the likely organism must be identified on initial presentation
Skin and soft-tissue infections
-
The WBC count and ESR are mildly or moderately elevated
-
If bullae are present, Gram stain and culture results from aspirated exudate from a bullous lesion may help identify the pathogen
-
Blood culture results may be positive
-
In suspected deep soft-tissue infection, plain radiography, computed tomography (CT) scanning, or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) may be performed to evaluate for compartment syndrome or for gas or a foreign body in the deep tissues; [1] excessive gas signifies a mixed aerobic-anaerobic infection, in contrast to gas gangrene (clostridial myonecrosis)
-
Gram stains and/or cultures of samples aspirated from deep-skin and soft-tissue infections may be used to identify the organism
Acute osteomyelitis
-
The WBC usually reveals leukocytosis, and the ESR is moderately or highly elevated [2]
-
Blood culture results are usually negative; when positive, the findings most frequently indicate the presence of S aureus
-
For affected long bones, plain radiographic findings generally become abnormal after 10-14 days; soft-tissue swelling and periosteal elevation are the earliest signs
-
Bone scans may be very useful if the plain radiograph is negative; bone-scan findings are positive within 24 hours; alternative imaging may include MRI or positron emission tomography (PET) scanning
-
Bone biopsy can considered but may not be needed if blood cultures are positive
Chronic osteomyelitis
-
The WBC count is often within the reference range; the ESR is usually very highly elevated and may exceed 100 mm/hr; [2] the platelet count is also often elevated
-
Osteomyelitis is more likely in patients with larger ulcers, visible bone or bone that can be probed, and elevated ESR
-
Blood culture results are usually negative
-
Plain radiographic findings are invariably abnormal
-
Bone scans are usually unnecessary unless diagnostic confusion exists with another disorder (eg, bone tumor); an MRI scan would also be helpful in such a situation
-
Bone biopsy performed under aseptic conditions in the operating room is the preferred way to identify the causative pathogen
-
Important pathogens include Bacteroides fragilis, Escherichia coli, Proteus mirabilis, and Klebsiella pneumoniae; Pseudomonas aeruginosa and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) also may be causative organisms
See Workup for more detail.
Management
Treatment of diabetic foot infections varies by type, as follows:
-
Cellulitis – Most responsive to antibiotics
-
Deep skin and soft-tissue infections – Usually curable, but additional debridement is usually indicated
-
Acute osteomyelitis – Infecting microorganisms and the likelihood of successful treatment with antimicrobial therapy are essentially the same as in patients without diabetes
-
Chronic osteomyelitis – Surgical debridement is essential, in addition to antibiotics; amputation may be necessary; assessment of the patient's vasculature may be required
See Treatment and Medication for more detail.
Background
Foot infections are the most common problems in persons with diabetes. These individuals are predisposed to foot infections because of a compromised vascular supply secondary to diabetes. Local trauma and/or pressure (often in association with lack of sensation because of neuropathy), in addition to microvascular disease, may result in various diabetic foot infections that run the spectrum from simple, superficial cellulitis to chronic osteomyelitis.
The radiograph below demonstrates a foot lesion in a patient with diabetes.
 Chronic diabetic ulceration with underlying osteomyelitis. Plain film radiograph exhibiting cortical disruption at the medial aspect of the first MTP joint.
Chronic diabetic ulceration with underlying osteomyelitis. Plain film radiograph exhibiting cortical disruption at the medial aspect of the first MTP joint.
Infections in patients with diabetes are difficult to treat because these individuals have impaired microvascular and at times macrovascular circulation, which limits the access of phagocytic cells to the infected area and results in a poor concentration of antibiotics in the infected tissues. In addition, diabetic individuals can not only have a combined infection involving bone and soft tissue called fetid foot, a severe and extensive, chronic soft-tissue and bone infection that causes a foul exudate, but they may also have peripheral vascular disease that involves the large vessels, as well as microvascular and capillary disease that results in peripheral vascular disease with gangrene. [3, 4, 5, 6, 7]
Except for chronic osteomyelitis, infections in patients with diabetes are caused by the same microorganisms that can infect the extremities of persons without diabetes. Gas gangrene is conspicuous because of its low incidence in patients with diabetes, but deep-skin and soft-tissue infections, which are due to gas-producing organisms, frequently occur in patients with these infections.
In general, foot infections in persons with diabetes become more severe and take longer to cure than do equivalent infections in persons without diabetes.
Staging in diabetic foot infections is applicable only in cases of chronic osteomyelitis that require surgery.
Go to Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus,Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus, and Diabetic Foot Ulcers to see more complete information on these topics.
Pathophysiology
In chronic osteomyelitis, a sequestrum and involucrum form; these represent islands of infected bone. Bone fragments that are isolated have no blood supply.
Bacteremia may accompany cellulitis, skin or soft-tissue infections, and/or acute osteomyelitis. If chronic osteomyelitis is left untreated for years, it may lead to complications such as amyloidosis or squamous cell carcinoma at the site of drainage through the skin. Bacteremia and septic shock rarely, if ever, occur as a result of chronic osteomyelitis.
Research indicates that when present in Staphylococcus aureus, the prophage ROSA-like inhibits the bacterium from infecting diabetic foot ulcers and also prevents S aureus from replicating inside osteoblasts, diminishing cell damage to these lesions. [8]
Etiology
Diabetes mellitus is a disorder that primarily affects the microvascular circulation. In the extremities, microvascular disease limits the blood supply to the superficial and deep structures. Pressure due to ill-fitting shoes or trauma further compromises the local blood supply at the microvascular level, predisposing the patient to infection, which may involve the skin, soft tissues, bone, or all of these combined.
Diabetes also accelerates macrovascular disease, which is evident clinically as accelerating atherosclerosis and/or peripheral vascular disease. Most diabetic foot infections occur in the setting of good dorsalis pedis pulses; this finding indicates that the primary problem in diabetic foot infections is microvascular compromise.
Impaired microvascular circulation hinders white blood cell migration into the area of infection and limits the ability of antibiotics to reach the site of infection in an effective concentration. Diabetic neuropathy may be encountered in conjunction with vasculopathy. This may allow for incidental trauma that goes unrecognized (eg, blistering, penetrating foreign body, Charcot foot). Go to Diabetic Neuropathy for more complete information on this topic.
Microbial characteristics
The microbiologic features of diabetic foot infections vary according to the tissue infected. In patients with diabetes, superficial skin infections, such as cellulitis, are caused by the same organisms as those in healthy hosts, namely group A streptococci and S aureus. In unusual epidemiologic circumstances, however, organisms such as Pasteurella multocida (eg, from dog or cat bites or scratches) may be noted and should always be considered. Group B streptococcal cellulitis is uncommon in healthy hosts but not uncommon in patients with diabetes. In diabetic individuals, group B streptococci may cause urinary tract infections and catheter-associated bacteriuria in addition to cellulitis, skin and/or soft-tissue infections, and chronic osteomyelitis. Such infections may be complicated by bacteremia.
Furthermore, as previously mentioned, deep soft-tissue infections in diabetic persons can be associated with gas-forming organisms. Clinically, these infections appear as necrotizing fasciitis, compartment syndrome, or myositis.
Acute osteomyelitis usually occurs as a result of foot trauma in an individual with diabetes. The distribution of organisms is the same as that in an individual without diabetes who has acute osteomyelitis. In chronic osteomyelitis, however, the pathogens include group A and group B streptococci, aerobic gram-negative bacilli, and anaerobic organisms.
Some of the pathogens implicated in chronic osteomyelitis in patients with diabetes include B fragilis, Escherichia coli, Proteus mirabilis, and Klebsiella pneumoniae.
MRSA and pseudomonads may be associated with diabetic foot infections.
Epidemiology
Globally, diabetic foot infections are among the most common skeletal and soft-tissue infections. The incidence of diabetic foot infections is similar to that of diabetes in various ethnic groups, and these infections most frequently affect elderly patients. There are no significant differences between the sexes.
Mortality is not common, except in unusual circumstances. The mortality risk is highest in patients with chronic osteomyelitis and in those with acute necrotizing soft-tissue infections.
A prospective cohort study by Lynar et al indicated that in patients with diabetic foot infections, the mortality risk is increased in those who are undergoing hemodialysis or of older age. The 1-year, cumulative mortality risk in patients receiving hemodialysis was determined to be 24.5%. [9]
Prognosis
The prognosis for cases of cellulitis, skin and/or soft-tissue infections, and acute osteomyelitis depends on the adequacy of antimicrobial therapy and surgical debridement. For cases of chronic osteomyelitis, the prognosis is directly related to the vascular supply in the affected limb and the adequacy of surgical debridement.
In a German study, nearly 250 patients with diabetic foot ulcers were evaluated and followed over time. Major adverse risk factors for long-term limb salvage included the presence of significant peripheral artery disease and renal insufficiency. [10]
A study by Chammas et al indicated that ischemic heart disease is the primary cause of premature death in patients with diabetic foot ulcer, finding it to be the major source of mortality on postmortem examination in 62.5% of 243 diabetic foot ulcer patients. The study also found that in patients with diabetic foot ulcer, the mean age of death from ischemic heart disease, as derived from postmortem examination, was 5 years below that of controls. Patients with neuropathic foot ulcers were determined to have the highest risk of premature death from ischemic heart disease. [11]
A study by Chen et al indicated that following hospital treatment for diabetic foot ulcer, invasive systemic infection associated with the ulcer (DFU-ISI) is an important late complication that increases mortality risk. In the study’s patients, methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) gave rise to 57% of the ISIs. Using Cox regression modeling, the investigators found that complicated ulcer healing and the presence of MRSA in the initial ulcer culture predicted the development of DFU-ISIs (hazard ratios of 3.812 and 2.030, respectively), with the hazard ratio for mortality risk in association with DFU-ISIs being 1.987. [12]
Patient Education
Patients with diabetes must be careful to avoid foot trauma and to properly care for their feet to minimize the possibility of infection. In addition, they must understand that chronic osteomyelitis cannot be cured with antibiotics alone and that adequate surgical debridement is necessary.
Patients who are unwilling to undergo the surgical procedure must understand the long-term complications of chronic osteomyelitis. They should be advised that if the infection is not adequately treated with sufficient surgical debridement and/or amputation, systemic complications, including bacteremia and/or systemic infection, amyloidosis, and squamous cell carcinoma at the affected site, may occur over time.
Long-term suppressive therapy may decrease the incidence of septic complications, but it does not affect the long-term complications, which may include amyloidosis or squamous cell carcinoma at the drainage site.
-
Chronic diabetic ulceration with underlying osteomyelitis. Plain film radiograph exhibiting cortical disruption at the medial aspect of the first MTP joint.








