Edith L. Potter. Facial characteristics of infants with bilateral renal agenesis. American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology. 1946. 51:885-888.
Fantel AG, Shepard TH. Potter syndrome. Nonrenal features induced by oligoamnios. Am J Dis Child. 1975 Nov. 129(11):1346-7. [QxMD MEDLINE Link].
Vanderheyden T, Kumar S, Fisk NM, et al. Fetal renal impairment. Semin Neonatol. 2003 Aug. 8(4):279-89. [QxMD MEDLINE Link].
Paces-Fessy M, Fabre M, Lesaulnier C, Cereghini S. Hnf1b and Pax2 cooperate to control different pathways in kidney and ureter morphogenesis. Hum Mol Genet. Apr/2012. 24:[QxMD MEDLINE Link]. [Full Text].
Guertl B, Senanayake U, Nusshold E, Leuschner I, Mannweiler S, Ebner B, et al. Lim1, an embryonal transcription factor, is absent in multicystic renal dysplasia, but reactivated in nephroblastomas. Pathobiology. 2011. 78(4):210-9. [QxMD MEDLINE Link]. [Full Text].
Wang SH, Wu CC, Lu YC, Lin YH, Su YN, Hwu WL, et al. Mutation screening of the EYA1, SIX1, and SIX5 genes in an east asian cohort with branchio-oto-renal syndrome. Laryngoscope. May/2012. 122(5):1130-6. [QxMD MEDLINE Link]. [Full Text].
Skinner MA, Safford SD, Reeves JG, Jackson ME, Freemerman AJ. Renal aplasia in humans is associated with RET mutations. Am J Hum Genet. Feb/2008. 82(2):344-51. [QxMD MEDLINE Link]. [Full Text].
Wynshaw-Boris A, Ryan G, Deng CX, Chan DC, Jackson-Grusby L, Larson D, et al. The role of a single formin isoform in the limb and renal phenotypes of limb deformity. Mol Med. Jun/1997. 3(6):372-84. [QxMD MEDLINE Link]. [Full Text].
Costantini F, Shakya R. GDNF/Ret signaling and the development of the kidney. Bioessays. Feb/2006. 28(2):117-27. [QxMD MEDLINE Link]. [Full Text].
Lu BC, Cebrian C, Chi X, Kuure S, Kuo R, Bates CM, et al. Etv4 and Etv5 are required downstream of GDNF and Ret for kidney branching morphogenesis. Nat Genet. Dec/2009. 41(12):1295-302. [QxMD MEDLINE Link]. [Full Text].
Tabatabaeifar M, Schlingmann KP, Litwin M, Emre S, Bakkaloglu A, Mehls O, et al. Functional analysis of BMP4 mutations identified in pediatric CAKUT patients. Pediatr Nephrol. Dec/2009. 24(12):2361-8. [QxMD MEDLINE Link]. [Full Text].
Gribouval O, Gonzales M, Neuhaus T, Aziza J, Bieth E, Laurent N, et al. Mutations in genes in the renin-angiotensin system are associated with autosomal recessive renal tubular dysgenesis. Nat Genet. 2005 Sep. 37(9):964-8. [QxMD MEDLINE Link].
Uematsu, M.Sakamoto, O.Nishio, T.Ohura, T.Matsuda, T.Inagaki, et al. A case surviving for over a year of renal tubular dysgenesis with compound heterozygous angiotensinogen gene mutations. Am J Med Genet A. 2006. 140:2355-60. [QxMD MEDLINE Link]. [Full Text].
Kumar, D.Moss, G.Primhak, R.Coombs, R. Congenital renal tubular dysplasia and skull ossification defects similar to teratogenic effects of angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors. J Med Genet. 1997. 34:541-5. [QxMD MEDLINE Link]. [Full Text].
Lambot, M. A.Vermeylen, D.Noel, J. C. Angiotensin-II-receptor inhibitors in pregnancy. Lancet. 2001. 357:1619-20. [QxMD MEDLINE Link]. [Full Text].
Lindner TH, Njolstad PR, Horikawa Y, Bostad L, Bell GI, Sovik O. A novel syndrome of diabetes mellitus, renal dysfunction and genital malformation associated with a partial deletion of the pseudo-POU domain of hepatocyte nuclear factor-1beta. Hum Mol Genet. 1999 Oct. 8(11):2001-8. [QxMD MEDLINE Link].
Nakayama M, Nozu K, Goto Y, Kamei K, Ito S, Sato H, et al. HNF1B alterations associated with congenital anomalies of the kidney and urinary tract. Pediatr Nephrol. 2010 Jun. 25(6):1073-9. [QxMD MEDLINE Link].
Schönfelder EM, Knüppel T, Tasic V, Miljkovic P, Konrad M, Wühl E, et al. Mutations in Uroplakin IIIA are a rare cause of renal hypodysplasia in humans. Am J Kidney Dis. 2006 Jun. 47(6):1004-12. [QxMD MEDLINE Link].
Hoefele J, Gabert M, Heinrich U, Benz K, Rompel O, Rost I, et al. A novel interstitial deletion of 10q24.2q24.32 in a patient with renal coloboma syndrome. Eur J Med Genet. March/2012. 55(3):211-5. [QxMD MEDLINE Link]. [Full Text].
Alazami AM, Shaheen R, Alzahrani F, Snape K, Saggar A, Brinkmann B, et al. FREM1 mutations cause bifid nose, renal agenesis, and anorectal malformations syndrome. Am J Hum Genet. 2009 Sep. 85(3):414-8. [QxMD MEDLINE Link]. [Full Text].
Pitera JE, Scambler PJ, Woolf AS. Fras1, a basement membrane-associated protein mutated in Fraser syndrome, mediates both the initiation of the mammalian kidney and the integrity of renal glomeruli. Hum Mol Genet. 2008 Dec 15. 17(24):3953-64. [QxMD MEDLINE Link].
van Haelst MM, Maiburg M, Baujat G, Jadeja S, Monti E, Bland E, et al. Molecular study of 33 families with Fraser syndrome new data and mutation review. Am J Med Genet A. 2008 Sep 1. 146A(17):2252-7. [QxMD MEDLINE Link].
Al-Hamed MH, Sayer JA, Alsahan N, et al. Novel loss of function variants in FRAS1 AND FREM2 underlie renal agenesis in consanguineous families. J Nephrol. 2020 Jul 8. [QxMD MEDLINE Link].
Li Y, Pawlik B, Elcioglu N, Aglan M, Kayserili H, Yigit G. LRP4 mutations alter Wnt/beta-catenin signaling and cause limb and kidney malformations in Cenani-Lenz syndrome. Am J Hum Genet. 2010 May 14. 86(5):696-706. [QxMD MEDLINE Link].
Cain JE, Islam E, Haxho F, Chen L, Bridgewater D, Nieuwenhuis E. GLI3 repressor controls nephron number via regulation of Wnt11 and Ret in ureteric tip cells. PLoS One. 2009. 4(10):e7313. [QxMD MEDLINE Link].
Miller EM, Hopkin R, Bao L, Ware SM. Implications for genotype-phenotype predictions in Townes-Brocks syndrome: case report of a novel SALL1 deletion and review of the literature. Am J Med Genet A. 2012 Mar. 158A(3):533-40. [QxMD MEDLINE Link].
Albuisson J, Pêcheux C, Carel JC, Lacombe D, Leheup B, Lapuzina P, et al. Kallmann syndrome: 14 novel mutations in KAL1 and FGFR1 (KAL2). Hum Mutat. 2005 Jan. 25(1):98-9. [QxMD MEDLINE Link].
Van Esch H, Groenen P, Nesbit MA, Schuffenhauer S, Lichtner P, Vanderlinden G, et al. GATA3 haplo-insufficiency causes human HDR syndrome. Nature. 2000 Jul 27. 406(6794):419-22. [QxMD MEDLINE Link].
McPherson E, Carey J, Kramer A, Hall JG, Pauli RM, Schimke RN, et al. Dominantly inherited renal adysplasia. Am J Med Genet. Apr/1987. 26(4):863-72. [QxMD MEDLINE Link].
Kirschen GW, Blakemore K, Al-Kouatly HB, et al. The genetic etiologies of bilateral renal agenesis. Prenat Diagn. 2024 Feb. 44 (2):205-21. [QxMD MEDLINE Link].
Curry CJ, Jensen K, Holland J, Miller L, Hall BD. The Potter sequence: a clinical analysis of 80 cases. Am J Med Genet. 1984 Dec. 19(4):679-702. [QxMD MEDLINE Link].
McPherson E. Renal anomalies in families of individuals with congenital solitary kidney. Genet Med. 2007 May. 9(5):298-302. [QxMD MEDLINE Link].
Slickers JE, Olshan AF, Siega-Riz AM, Honein MA, Aylsworth AS. Maternal body mass index and lifestyle exposures and the risk of bilateral renal agenesis or hypoplasia: the National Birth Defects Prevention Study. Am J Epidemiol. 2008 Dec 1. 168(11):1259-67. [QxMD MEDLINE Link].
Slickers JE, Olshan AF, Siega-Riz AM, Honein MA, Aylsworth AS. Maternal body mass index and lifestyle exposures and the risk of bilateral renal agenesis or hypoplasia: the National Birth Defects Prevention Study. Am J Epidemiol. 2008 Dec 1. 168(11):1259-67. [QxMD MEDLINE Link].
Wiesel A, Queisser-Luft A, Clementi M, et al. Prenatal detection of congenital renal malformations by fetal ultrasonographic examination: an analysis of 709,030 births in 12 European countries. Eur J Med Genet. 2005 Apr-Jun. 48(2):131-44. [QxMD MEDLINE Link].
Garne E, Loane M, Dolk H. Prenatal diagnosis of severe structural congenital malformations in Europe. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2005 Jan. 25(1):6-11. [QxMD MEDLINE Link].
Woods AG, Brandon DH. Prune belly syndrome. A focused physical assessment. Adv Neonatal Care. 2007 Jun. 7(3):132-43; quiz 144-5. [QxMD MEDLINE Link].
Klaassen I, Neuhaus TJ, Mueller-Wiefel DE, Kemper MJ. Antenatal oligohydramnios of renal origin: long-term outcome. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2007 Feb. 22(2):432-9. [QxMD MEDLINE Link].
Prouty LA, Myers TL. Oligohydramnios sequence (Potter's syndrome): case clustering in northeastern Tennessee. South Med J. 1987 May. 80(5):585-92. [QxMD MEDLINE Link].
Kadhim HJ, Lammens M, Gosseye S, et al. Brain defects in infants with Potter syndrome (oligohydramnios sequence). Pediatr Pathol. 1993 Jul-Aug. 13(4):519-36. [QxMD MEDLINE Link].
Preus M, Kaplan P, Kirkham TH. Renal anomalies and oligohydramnios in the cerebro-oculofacio-skeletal syndrome. Am J Dis Child. 1977 Jan. 131(1):62-4. [QxMD MEDLINE Link].
Greenwood RD, Rosenthal A, Nadas AS. Cardiovascular malformations associated with congenital anomalies of the urinary system. Observations in a series of 453 infants and children with urinary system malformations. Clin Pediatr (Phila). 1976 Dec. 15(12):1101-4. [QxMD MEDLINE Link].
Tonni G, Azzoni D, Ventura A, Ambrosetti F, De Felice C. "Multicystic dysplastic kidney (Potter type II syndrome) and agenesis of corpus callosum (ACC) in two consecutive pregnancies: a possible teratogenic effect of electromagnetic exposure in utero". Fetal Pediatr Pathol. 2008. 27(6):264-73. [QxMD MEDLINE Link].
Pramanik AK, Altshuler G, Light IJ, Sutherland JM. Prune-belly syndrome associated with Potter (renal nonfunction) syndrome. Am J Dis Child. 1977 Jun. 131(6):672-4. [QxMD MEDLINE Link].
Ginsberg J, Buchino JJ, Menefee M, et al. Multiple congenital ocular anomalies with bilateral agenesis of the urinary tract. Ann Ophthalmol. 1979 Jul. 11(7):1021-9. [QxMD MEDLINE Link].
Hall JG. Oligohydramnios sequence revisited in relationship to arthrogryposis, with distinctive skin changes. Am J Med Genet A. 2014 Nov. 164A(11):2775-92. [QxMD MEDLINE Link].
Schmidt W, Kubli F. Early diagnosis of severe congenital malformations by ultrasonography. J Perinat Med. 1982. 10(5):233-41. [QxMD MEDLINE Link].
Strauss A, Hasbargen U, Paek B, et al. [Prenatal diagnosis of kidney parenchyma diseases]. Z Geburtshilfe Neonatol. 2001 Mar-Apr. 205(2):71-5. [QxMD MEDLINE Link].
Yoshimura S, Masuzaki H, Miura K, et al. Diagnosis of fetal pulmonary hypoplasia by measurement of blood flow velocity waveforms of pulmonary arteries with Doppler ultrasonography. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1999 Feb. 180(2 Pt 1):441-6. [QxMD MEDLINE Link].
Hawkins JS, Dashe JS, Twickler DM. Magnetic resonance imaging diagnosis of severe fetal renal anomalies. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2008 Mar. 198(3):328.e1-5. [QxMD MEDLINE Link].
Fisk NM, Ronderos-Dumit D, Soliani A, Nicolini U, Vaughan J, Rodeck CH. Diagnostic and therapeutic transabdominal amnioinfusion in oligohydramnios. Obstet Gynecol. Aug/1991. 78(2):270-8. [QxMD MEDLINE Link]. [Full Text].
Raboei EH. The role of the pediatric surgeon in the perinatal multidisciplinary team. Eur J Pediatr Surg. 2008 Oct. 18(5):313-7. [QxMD MEDLINE Link].
Miller JL, Baschat AA, Rosner M, et al. Neonatal Survival After Serial Amnioinfusions for Bilateral Renal Agenesis: The Renal Anhydramnios Fetal Therapy Trial. JAMA. 2023 Dec 5. 330 (21):2096-105. [QxMD MEDLINE Link]. [Full Text].
Rani R, Cameron A, Munro F. Prenatal diagnosis and management of urethral obstruction. J Obstet Gynaecol Res. 1997 Feb. 23(1):59-62. [QxMD MEDLINE Link].
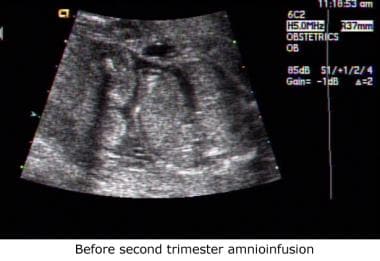 Sonogram obtained before second-trimester amnioinfusion. This fetus has bilaterally absent kidneys consistent with a diagnosis of Potter syndrome. The cystic structures in the renal fossae are most likely the adrenal glands.
Sonogram obtained before second-trimester amnioinfusion. This fetus has bilaterally absent kidneys consistent with a diagnosis of Potter syndrome. The cystic structures in the renal fossae are most likely the adrenal glands.

