Background
Splints are generally applied to decrease movement so as to provide support and comfort through stabilization of an injury. The primary purpose of a splint is to serve as a temporary bridge for nonemergency injuries to bones until definitive casting can be performed by a consultant, such as an orthopedic surgeon. Splints can also serve as initial immobilization in the preoperative period or as immobilization for primary healing. [1, 2, 3]
All patients with injuries that are splinted should be referred for evaluation by a consultant in a timely fashion, usually within 2-3 days.
Indications
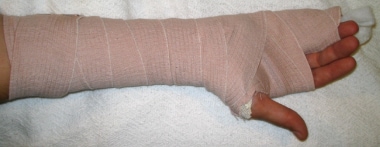
An ulnar gutter splint (see the image below) can be used for various injuries to the upper extremities, including the following:
-
Soft-tissue hand injuries to the fourth and fifth fingers
-
Fourth and fifth metacarpal fractures [4]
-
Fractures of the fourth and fifth phalanges
-
Positioning for rheumatoid arthritis or osteoarthritis [5]
Contraindications
Although no true contraindications for the placement of a splint are recognized, certain injuries require immediate evaluation or intervention by a consultant (eg, an orthopedic surgeon, hand surgeon, or plastic surgeon) and therefore may not necessitate splinting. Such injuries include the following:
-
Complicated fractures
-
Open fractures
-
Injuries with associated neurovascular compromise
-
Metacarpal angulation - In an otherwise uncomplicated metacarpal fracture, 10° of angulation is acceptable in the second and third metacarpals, 20° in the fourth, and 30° in the fifth; greater angulation often necessitates surgery, and such injuries require immediate evaluation or intervention by a consultant
-
Equipment for ulnar gutter splint. Image courtesy of Kenneth R Chuang, MD.
-
Ulnar gutter splinting: appropriate coverage of patient. Video courtesy of Kenneth R Chuang, MD.
-
Ulnar gutter splinting: removal of jewelry and rings to avoid ischemia from swelling. Video courtesy of Kenneth R Chuang, MD.
-
Ulnar gutter splinting: application of stockinette. Video courtesy of Kenneth R Chuang, MD.
-
Ulnar gutter splinting: application of cotton padding. Video courtesy of Kenneth R Chuang, MD.
-
Ulnar gutter splinting: measurement of dry plaster. Video courtesy of Kenneth R Chuang, MD.
-
Ulnar gutter splinting: wetting of plaster. Video courtesy of Kenneth R Chuang, MD.
-
Ulnar gutter splinting: application of wet plaster. Video courtesy of Kenneth R Chuang, MD.
-
Ulnar gutter splinting: application of bandage wrap. Video courtesy of Kenneth R Chuang, MD.
-
Ulnar gutter splinting: assessment of neurovascular function and capillary refill. Video courtesy of Kenneth R Chuang, MD.
-
Ulnar gutter splinting: molding of splint. Video courtesy of Kenneth R Chuang, MD.
-
Ulnar gutter splint. Image courtesy of Kenneth R Chuang, MD.